LoRa coverage: Four Data solutions for reliable, scalable connectivity of connected objects
At Four Data, we support companies in managing and optimizing their connected objects through our IoT management platform. Connectivity is a key issue for the collection, analysis and exploitation of data from connected sensors.
Today, the LoRaWAN network is one of the main solutions for connecting sensors and equipment over long distances, while guaranteeing low energy consumption. However, before adopting it, it’s essential to understand its scope, limitations and alternatives.

We’re here to listen!

What is LoRa technology and how does it work?
LoRa (Long Range) is a radio transmission technology designed to enable IoT sensors to communicate over long distances with low power consumption.
Unlike cellular networks, LoRa uses modulation based on chirp spread spectrum (CSS), which ensures greater resistance to interference and efficient transmission in complex environments (industrial, urban, agricultural), especially when signals are relayed by strategically placed antennas, without the need for a permanent Internet connection.
LoRa also stands out for its ability to deploy a private network. A company can install its own LoRaWAN gateways and manage its communications without depending on a third-party operator. This flexibility is a major asset for sectors requiring reliable, independent connectivity.
LoRa and LoRaWAN: what are the differences?
The distinction between LoRa and LoRaWAN is based on their function in communication networks for connected objects. LoRa is the radio technology that ensures long-range transmission, while LoRaWAN is the communication protocol that structures and secures exchanges between sensors and servers. Thanks to LoRaWAN, data can be encrypted, organized and transmitted efficiently to connected platforms, without the need for a constant Internet connection.
Current LoRa network coverage in France
The LoRaWAN network is widely deployed in France, mainly via Orange and Bouygues, which offer nationwide coverage enabling sensors to transmit data without being permanently dependent on the Internet. However, some isolated rural or industrial areas may be less well served.
Topography and infrastructure density strongly influence coverage quality. Metallic buildings, mountains or urban density can limit signal range, necessitating the installation of additional gateways to guarantee optimal connectivity. Understanding the factors that influence LoRa coverage is essential to optimizing its deployment. Here are the main elements to consider:
Map of LoRa coverage in France
LoRa network coverage varies by region and by operators such as Bouygues, directly influencing the ability of devices to transmit data efficiently. Large conurbations and industrial hubs benefit from good coverage, while some rural or mountainous areas may be less well served. Installing gateways or a LoRaWAN antenna can significantly improve connectivity.
➡ Need to check network coverage at your site? Four Data has developed a LoRa and Sigfox coverage test toolThis intuitive tool helps you identify potential white zones and optimize your IoT deployment. This intuitive tool helps you identify potential white zones and optimize your IoT deployment.
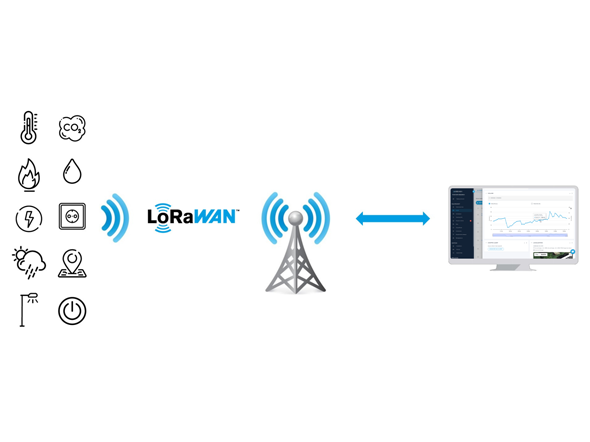
Factors influencing coverage
- Relief and urbanization: buildings and natural obstacles can attenuate the signal
- Gateway density and antenna positioning: a denser, well-placed infrastructure improves connectivity.
- Frequencies used: 868 MHz in Europe, 915 MHz in North America
International availability
Thanks to its availability in over 25 countries, LoRaWAN is a strategic choice for companies wishing to develop IoT solutions on an international scale. At Four Data, we support companies in integrating these technologies to make the most of the LoRaWAN coverage available in each country and ensure reliable connectivity between their connected objects.

What are the solutions for areas not covered by LoRa?
Although the LoRaWAN network covers a large part of France, some rural or isolated areas remain poorly served. For companies and local authorities requiring connectivity for their connected objects in these areas, several alternatives exist.
What are the alternatives to the LoRa network?
There are several technologies available for connecting communicating objects in areas where the LoRaWAN network is absent or inadequate. Some solutions, such as the deployment of private LoRa networks, require the addition of suitable gateways, while others, such as NB-IoT or LTE-M, rely on existing cellular infrastructures.
| Technology | Range | Flow | Consumption | Benefits | Disadvantages |
| Sigfox | 10-50 km | Very low | Very low | Broad coverage, low cost | Proprietary network, limited throughput |
| NB-IoT | A few km | Medium | Low | Good indoor penetration, existing cellular infrastructure | Higher power consumption than LoRa |
| LTE-M | A few km | High | Average | 4G/5G compatible, low latency | Higher consumption |
| Wi-Fi / BLE | 10-100m | High | High | Easy access, good throughput | Short range, dense infrastructure required |
| 5G IoT | 1-10 km | Very high | Average | Low latency, high throughput | Costly infrastructure, energy consumption |
What is the Sigfox network?
This IoT solution is a low-power, long-range communication technology for connected objects, operating on a proprietary global infrastructure. Unlike LoRa, which can be deployed as a private network, this technology relies on a single operator and requires a covered area to operate.
With a presence in over 70 countries, Sigfox is ideal for connected devices requiring infrequent data transmission (logistics tracking, environmental sensors, telemetry).
How does the Sigfox network work?
This network uses a radio modulation technology called Ultra Narrow Band (UNB), which enables signals to be transmitted over very narrow frequency bands. This guarantees robustness against interference and efficient transmission over long distances, with reduced energy consumption.
This communication protocol is based on a predominantly unidirectional model, where sensors send their data to base stations, but can receive very few instructions in return. This mode of operation is particularly suited to periodic readings and to connected objects requiring several years’ maintenance-free autonomy, while guaranteeing secure transmission of information.
On the other hand, it has certain limitations: its throughput is very low (12 bytes per message, up to 140 messages per day), and as its network is proprietary, it does not offer the possibility of deploying a private infrastructure. It is therefore particularly suited to applications requiring little communication and low cost, but can be restrictive for more advanced uses requiring regular two-way exchanges.
LoRa vs Sigfox comparison: which network to choose for your needs?
LoRaWAN and Sigfox are often compared because they target similar uses: the long-range, low-power connection of connected objects. However, there are fundamental differences between these technologies.
Technical differences between LoRa and Sigfox
| Criteria | LoRaWAN | Sigfox |
| Model | Open network, privately deployable | Proprietary network |
| Range | 2-15 km (rural) | 10-50 km (rural) |
| Data rate | 0.3 to 50 kbps | 0.1 kbps |
| Bi-directional | Yes (sensor-server exchanges) | Very limited |
| Consumption | Very low | Very low |
| Subscription cost | Variable according to operator or private | Fixed according to Sigfox |
| Typical use cases | Smart cities, agriculture, industry | Tracking, predictive maintenance |
LoRaWAN is more flexible and suited to private networks requiring high interactivity, with the possibility of adding local antennas to boost coverage, while Sigfox is simple to deploy and ideal for devices sending little data.
Applications and challenges of the LoRa network for connected devices
What are the main uses of the LoRa network?
The LoRa network is particularly well suited to environments requiring wide-range connectivity and low energy consumption. Its use is rapidly expanding in a number of strategic sectors, notably for industrial applications, infrastructure management and energy consumption optimization.
In industry, LoRa technology is used for equipment monitoring and predictive maintenance. By monitoring installations, it helps anticipate breakdowns and optimize inventory management or technical interventions.
More broadly, LoRa can be deployed in many areas where long-range, low-power connectivity is strategic, such as urban infrastructure, agriculture or healthcare. For example, some regions use it to optimize parking, monitor air quality or control public lighting. In the agricultural sector, LoRa facilitates crop monitoring, irrigation management and herd tracking. It can also be used to remotely monitor patients via connected medical devices.
Finally, logistics and transport also benefit greatly from this technology. LoRa enables goods to be tracked throughout the supply chain, guaranteeing better traceability and optimizing routes to reduce costs and lead times.
What are the challenges of deploying the LoRa network?
While LoRa offers undeniable advantages, there are certain limitations that need to be taken into account to ensure effective deployment.
One of the first challenges is interoperability. Although LoRaWAN is an open protocol, its adoption varies from country to country and from operator to operator. It is essential to ensure that equipment and software are compatible to avoid any technical constraints.
Network coverage is another decisive factor. While large conurbations benefit from good network coverage, rural or industrial areas can be poorly served. To overcome this problem, some companies are deploying private LoRaWAN gateways, which represent an additional investment.
Sidebar: Security and data protection on the LoRa network
Securing transmissions is a key aspect of LoRa deployment. Although the LoRaWAN protocol incorporates data encryption, several risks need to be anticipated:
- Sensor vulnerability: LoRa connected objects are often deployed outdoors and can be physically compromised. It is essential to secure their access and updates.
- Gateway protection: A poorly configured gateway can become a security vulnerability. We recommend strengthening authentication and isolating these devices from the rest of the network.
- Data encryption: LoRaWAN uses AES-128 to protect exchanges, but attacks are still possible if keys are not properly managed.
- Prevention of replay attacks: Some connectivity protocols are vulnerable to replay attacks, in which a signal is intercepted and retransmitted to deceive the system. LoRaWAN incorporates frame counters to prevent these scenarios.
Implementing a security plan for connected objects using LoRa technology is essential, especially when transmitting sensitive information over long distances, to guarantee the integrity and confidentiality of communications.
Finally, the rapid evolution of technologies raises the question of LoRa’s sustainability in the face of emerging alternatives such as 5G or NB-IoT. Companies need to assess the relevance of their technological choice in terms of their long-term needs and market trends.
FAQ : Tank level gauges and sensors
Additional resources
How do you choose the best IoT solution for your needs?
The choice of a connectivity solution depends on several criteria:
- Coverage area: check whether LoRaWAN covers the area of use, or whether an alternative should be considered.
- Energy consumption: LoRa is ideal for sensors requiring extended autonomy.
- Volume of data to be transmitted: if high throughput is required, technologies such as LTE-M or 5G may be more suitable.
- Deployment costs: a private LoRa network may be more costly to install, but profitable over time.
Before opting for LoRa or an alternative, we recommend carrying out an audit of connectivity needs to assess the best solution.
Useful resources to learn more about LoRa coverage
To find out more, here are some useful resources:
- Interactive maps of LoRa coverage in France and other countries.
- Official LoRaWAN Alliance guides on the network’s technical specifications.
- Case studies of companies that have successfully deployed LoRaWAN.
Four Data support

At Four Data, we know that the connectivity of a LoRaWAN network directly impacts the performance and reliability of your connected device projects, by ensuring a good signal and adequate coverage. Infrastructure monitoring, logistics optimization, energy efficiency: the right network coverage is essential.
Our IoT management platform helps you make the most of your sensors, whatever technology you use (LoRaWAN, Sigfox, NB-IoT, LTE-M). We support you from needs analysis to data exploitation, with feasibility studies, real-life tests (POC) and personalized follow-up for reliable, long-term deployment.
Thanks to our flexible, adaptable approach, we design tailor-made solutions for industry, energy, transport, smart cities, agriculture and intelligent buildings.
Need a private LoRa network, multi-technology integration or coverage optimization? Contact us today to design your connected infrastructure.
If you have a request or a question, click here: